Vaccine banks
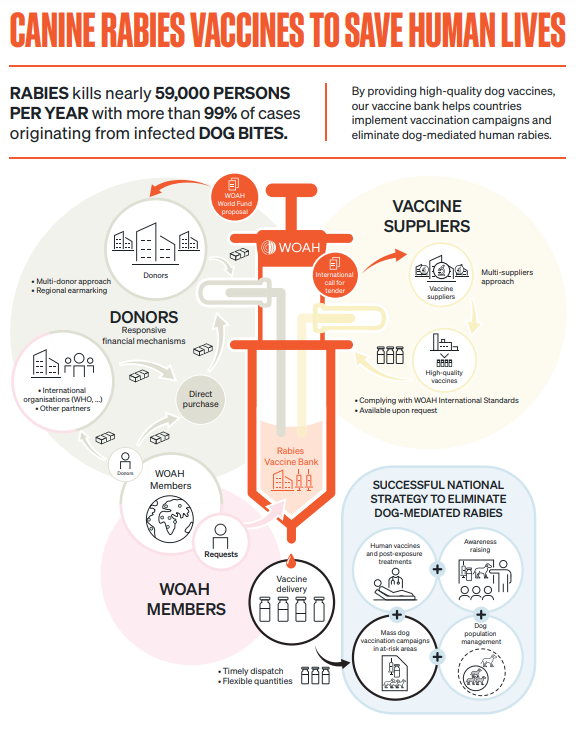
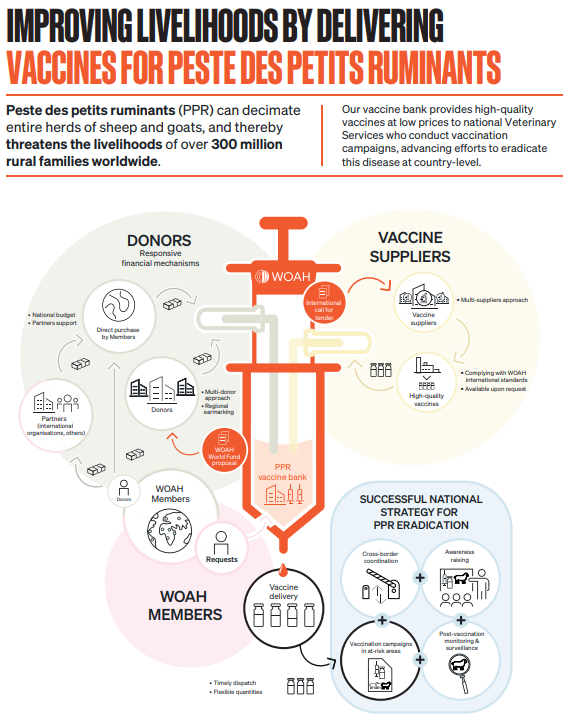
Vaccine banks ensure the procurement of high quality vaccines manufactured in line with WOAH intergovernmental standards and delivered in a timely manner. Vaccine banks enable economies of scale and contribute to the harmonisation of global and regional control programmes. As of January 2023, two WOAH vaccine banks are active and focus on rabies and peste des petits ruminants (PPR).

The WOAH World Fund has worldwide experience in the management of vaccine banks and the delivery of vaccines for avian influenza (AI), foot-and-mouth disease (FMD), rabies (vaccination of dogs), and peste des petits ruminants (PPR).
When quality vaccines are provided to developing countries at the airport of destination, the beneficiary country can concentrate its efforts and resources on implementing the vaccination campaigns (mobilisation of human, financial and technical resources, such as staff for vaccination, cold chain transport and storage, vaccination consumables, and follow-up on vaccination campaigns), or on contracting public/private partnerships with implementing partners such as NGOs.
The use of the vaccine bank mechanism encourages beneficiary countries to act and creates leverage effects when these countries decide to fund animal disease control programmes and implement them efficiently. Vaccine banks enable economies of scale, synergies and leveraging of results while contributing to harmonisation and coordination of global and regional control programmes. In addition, they allow for multi-party vaccination campaigns, public–private partnerships and the possible involvement of non-governmental organisations.
Operation
WOAH vaccine banks are established through international calls for tender and selection procedures involving independent committees composed of international experts (WOAH reference laboratories) and donor representatives.
They can be activated only upon request from the country, through the WOAH Delegate who sends an official request to the Director General of the WOAH.
WOAH regional antigen/vaccine banks may include ready-to-use, formulated vaccines which can be delivered in a timely manner if urgent requests arise. Production can also be organised on demand with possible replenishment mechanisms in order to meet the needs of a variety of different orders. This mechanism enables the rapid supply of emergency stocks of vaccines to affected countries, as well as planned deliveries at a lower cost, in order to vaccinate targeted animal populations at risk and to eventually target eradication wherever possible.
Funding
To date, the creation of vaccine banks, as well as vaccines delivered afterwards, have been supported financially by Australia (FMD and Rabies), Canada (AI and Rabies), China (FMD), the European Union (AI, FMD and Rabies), France (Rabies and FMD), Germany (Rabies), Japan (Rabies), the Republic of Korea (FMD), New Zealand (FMD), the World Bank (PPR) and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (PPR).
Generally, WOAH vaccine bank contracts include possible clauses for direct purchase by beneficiary countries or by international organisations and partners.
Considering the efficiency of the WOAH mechanism for procurement of vaccines, WHO decided in 2014 to place all of its orders for rabies vaccines for dogs through the WOAH Rabies Vaccine Bank.
This has enabled the delivery by WHO of 16.3 million doses of rabies vaccines, as of January 2022.
History
In 2006, WOAH set up a first regional vaccine bank of Avian Influenza vaccines in Africa funded under the European Union Pan African Programme for the Control of Epizootics (PACE) and in 2007 enlarged this vaccine bank to a global scale (opening it to Asian countries) thanks to Canadian funds.
H5N2 doses were delivered to multiple countries, including in kind donations from the United Kingdom and Canada. The Avian Influenza vaccine bank is now closed, but through these financial supports:
- 62,017 million H5N2 doses were delivered to the following countries: Mauritania, Senegal, Egypt, Mauritius, Ghana, Togo and Vietnam
- 28 million H5N2 doses were distributed in Egypt, making it the country that received the most significant level of distribution
- 26.7 million H5N2 doses were distributed in Vietnam, making it the second country to receive the most significant level of distribution
The European Union funded Regional Cooperation Programme on Highly Pathogenic Emerging and Re-emerging animal diseases (HPED), that had commenced in 2010, has seen the expansion of WOAH’s vaccine bank concept to other diseases, adding Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) and rabies (vaccination of dogs) in Asian countries. The initial target was to rapidly (emergency) provide eligible countries with a stock of vaccines to vaccinate animal populations at risk under the framework of agreed vaccination. This is how were created the WOAH vaccine bank for FMD in 2011 and the Rabies vaccine bank in 2012.
The antigens reserved for FMD are mainly designed to be used for strategic vaccination in buffer zones (ring vaccination) and hot spots around disease-free areas in order to stop the spread of the disease, as well as to reduce the associated economic costs caused by the loss of FMD free status. Besides the European Union, additional financial support has been received from Australia, China, New Zealand and the Republic of Korea for the procurement of FMD vaccines to eligible countries. This has demonstrated the multi-donor approach supporting the concept of regional vaccine banks. The FMD antigen bank is now closed.
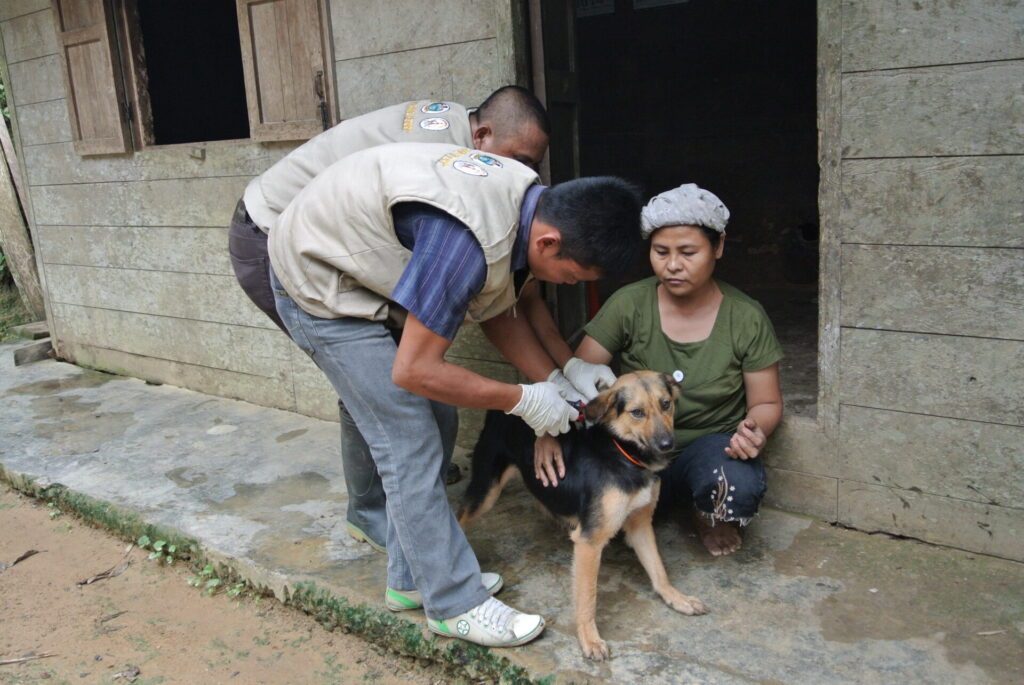
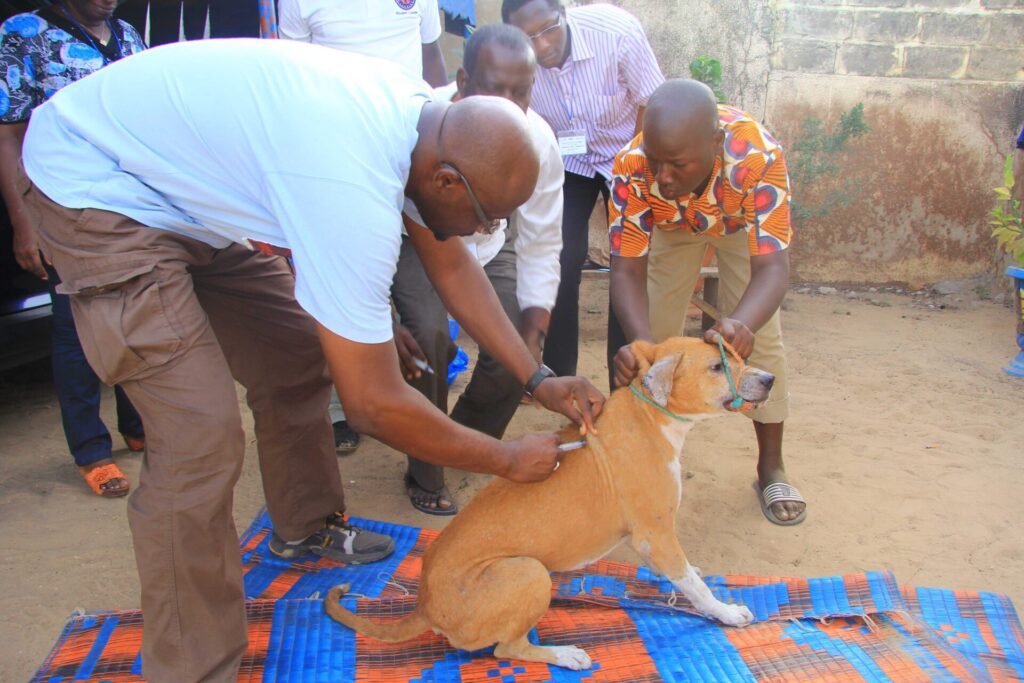
With reference to rabies, WOAH vaccine bank supports the delivery of injectable rabies vaccines for dogs to eligible countries. The elimination of rabies is both a public health and economic priority and, hence, preventing the spread of this zoonotic disease is essential in order to reduce the number of human deaths and the socio-economic cost of the post contamination treatment of humans. Dog vaccination against rabies is the only way to break the cycle of transmission among dogs and between dogs and humans. After Asia, WOAH rabies vaccine bank was opened to eligible countries in Africa, with additional financial supports from France, Germany and the European Union.
In 2013, a PPR vaccine bank for Africa was established for the provision of high quality PPR vaccines to eligible African countries. Funding support for the PPR vaccine bank for Africa was provided by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. This vaccine bank not only ensures the timely supply of high quality vaccines complying with international standards, but also facilitates the harmonisation of PPR control methods in Africa. The World Bank has also provided support to the WOAH PPR vaccine bank for Africa through the Regional Sahel Pastoralism Support Project (PRAPS) which targets 6 countries in Western and Central Africa.
Number of doses delivered as of September 2024
28.9 million
rabies vaccine doses delivered to countries in Africa and Asia.
8.1 million
foot and mouth disease vaccine doses delivered to countries in Africa.
* A delivery of 100 000 rabies vaccine doses to Haiti was exceptionally made thanks to Canadian funds.
** A delivery of 500 000 FMD disease vaccine doses to Algeria was exceptionally made thanks to World Bank funds.